Elephant Beetle steals millions of dollars from organizations worldwide

A threat actor that goes by the name ‘Elephant Beetle’ is using a combination of around 80 tools to steal millions of dollars from enterprises across the world.
This is a blase act as the group studies the victim’s network and environment patiently including the financial transactions, and then starts to exploiting the network with the flaws and loopholes identified.
The criminals introduce fake transactions into the environment and then steal small amounts over a long period, thus hiding the actual theft and keeping it calm. If in case these actions are spotted they continue to stay in the network but do not perform any further activities but later repeat the same with different method.
What is an Elephant Beetle?
Elephant Beetle targets legacy Java applications on Linux devices, and focuses on known vulnerabilities that are left unpatched. This was discovered by the Sygnia Incident Response team and has been published in detail in their report.
Elephant Beetle leverages the following four vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code remotely via a specially designed web shell, SAP NetWeaver Invoker Servlet Exploit (CVE-2010-5326) and Config Servlet Remote Coed Execution (EDB-ID-24963), WebSphere Application Server SOAP Exploit (CVE-2015-7450) and Primefaces Application Expression Language Injection (CVE-2017-1000486). Once they breach the network, their next checkpoint is to stay invisible and study the environment, this will be done over a period of months.
They stay undetected by behaving in a normal way and sync with the normal traffic to be legitimate source and use WAR archives to prepare the payloads. These actors will then slowly start becoming more of a parasite by manipulating the files, and prepare for their attack.
How is Elephant Beetle spread laterally within a network?
The actors use a custom-made Java scanner that gets IP addresses for a HTTP or Specific Port. This custom-made scanner is versatile and can be personalized as per the actors mission, later, they figure out the best internal server points and compromise it using stolen credentials or using RCE vulnerability and spread further laterally within the network.
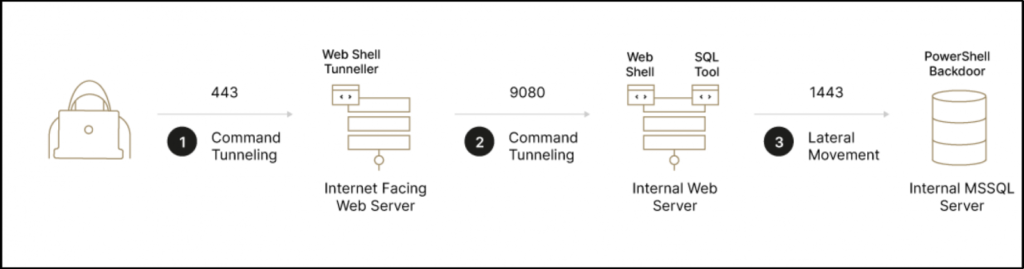
As per the Sygnia report, the lateral movement is achieved using the SQL and Web Application Servers using Windows APIs and xp_cmdshell with remote execution backdoors. Also, it is reported that the actors use multiple backdoors to achieve their goal.
Defending against Elephant Beetle
The C2 of Elephant Beetle operation is based out of Mexico and the actors use multiple Spanish Code Variables and References which emphasizes the same. And the custom-made scanner was uploaded from Argentina which confirms the groups origin should be from the LATAM.
Here’s what you should do to avoid Elephant Beetle threat,
- Do not use xp_cmdshell and shutdown the MS-SQL servers. Monitor the changes in the use of xp_cmdshell and the configurations.
- Check WAR activities and validate the deployment of packages and their functionality is associated with logging.
- Verify the isolation between your internal servers and the DMZ.
- Verify your WebSphere apps’s temp folders for malicious .class file.
- Patch those unpatched applications immediatley as Elephant Beetle is targeting old unpatched vulnerabilities.
Read through the Sygnia report to understand the Indicator of Compromise which will assist in detecting Elephant Beetle’s presence proactively.
Subscribe to our newsletter for daily alerts on cyber events, you can also follow us on Facebook, Linkedin, Instagram, Twitter and Reddit.
You can reach out to us via Twitter or Facebook, for any advertising requests.





