Graphic Card Fingerprinting is manipulated to track user’s activity on the web

A new fingerprinting technique is exploiting a device’s graphics processing unit (GPU) that can track users activity on the web persistently. This technique is called as DrawnApart, and identifies as a device from the unique properties of the the GPU.
This is identified by researchers from Australia, Israel and France mentioned in their paper that the technique adds variations in speed among the multiple executions units that compromise a GPU can serve a reliable and robust device signature, which is collected using unprivileged JavaScript.
What is Fingerprinting?
The process of collecting information about device’s hardware, installed software, web browsers, and add-ons using a remote device for unique identification is called Fingerprinting.
This technique can be a double-edged sword as well. It can be used for identifying the theft and detect fraudulent behavior. However, it can also be used for compiling long-term records of users browsing activities for improved advertising. Browser fingerprinting depends on aligning key attributes of information of the browser data to create a fingerprint. The attributes include browser version, OS, timezone, language, screen, list of fonts, rendering text and graphics.
However, since browser fingerprints are harder to track for long time, the DrawnApart makes it a possibility.
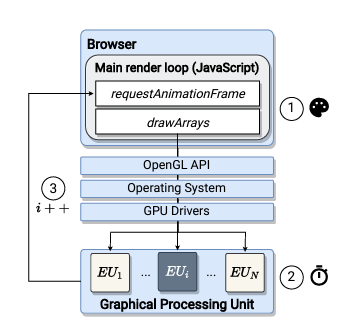
How does fingerprinting exploit the GPU stack?
The DrawnApart tracking mechanism involves the measuring the time needed for rendering different graphic primitives using the WebGL API targeting various execution units that forms a GPU creating a fingerprint trace which is then injected into a deep learning network to identify the device that generates it.
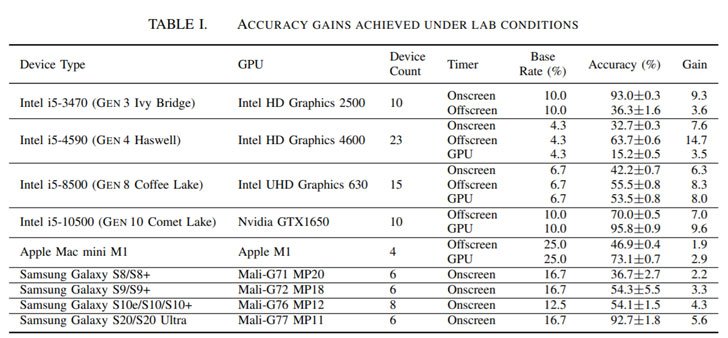
GPU Fingerprinting testing and evaluation
In an experiment 88 devices with Windows 10, Mac and multiple Samsung Galaxy smartphones were used in conjunction with fingerprint linking algorithms like FP-STALKER, and the researchers figured out that the average tracking period is 17.5-28 days.
Mitigating this GPU fingerprinting technique
To counter the GPU fingerprinting mechanism employing script blocking, disabling WebGL, and limiting each web page to a single execution unit, or even turning off hardware-accelerated rendering is recommended by researchers as the same could severely affect usability and responsiveness.
Also, the ongoing development in WebGPU standards that are in canary releases of Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome can reduce the time tracking duration of fingerprinting, and these effects on accelerated compute APIs on user privacy has to be considered before they are enabled globally.
Subscribe to our newsletter for daily alerts on cyber events, you can also follow us on Facebook, Linkedin, Instagram, Twitter and Reddit.
You can reach out to us via Twitter or Facebook, for any advertising requests.





