Scattered Spider: FBI and CISA Issue Warning on Elusive Cyber Threat

The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) have jointly warned regarding the elusive threat entity Scattered Spider.
Collaborating with the ALPHV/BlackCat Russian ransomware operation, this loosely connected hacking collective has recently gained attention for its sophisticated tactics.
What is Scattered Spider?
Scattered Spider, also recognized by aliases such as 0ktapus, Starfraud, UNC3944, Scatter Swine, Octo Tempest, and Muddled Libra, is proficient in social engineering and employs techniques like phishing, multi-factor authentication (MFA) bombing, and SIM swapping to infiltrate large organizations.
Comprising English-speaking members, some as young as 16, with diverse skill sets, the group frequents hacker forums and Telegram channels. Certain members are suspected to be part of the “Comm,” a loosely connected community involved in both cyber incidents and violent acts, garnering widespread media attention.
Contrary to the perception of a cohesive gang, Scattered Spider operates as a network of individuals, with different actors participating in each attack. This decentralized structure poses challenges in tracking their activities. Despite the FBI having knowledge of at least 12 members, none have been indicted or arrested.
Scattered Spider’s notorious activities
Scattered Spider’s activities have been documented since the previous summer, with cybersecurity company Group-IB reporting attacks aimed at stealing Okta identity credentials and 2FA codes.
In December 2022, CrowdStrike characterized the group as a financially motivated entity targeting telecommunications companies. Their tactics involve high-level social engineering, defense reversal, and the use of various software tools.
In January 2023, Crowdstrike uncovered Scattered Spider’s use of “Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver” (BYOVD) methods to evade detection from endpoint detection and response (EDR) security products.
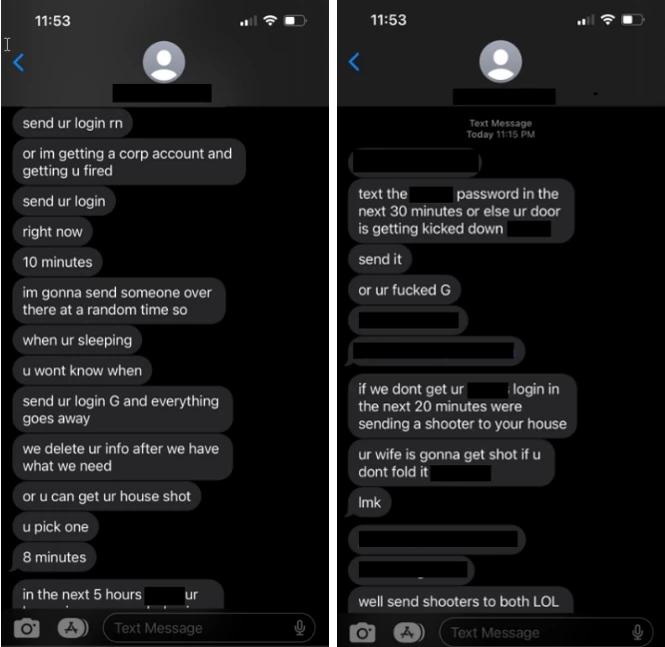
Recent high-profile attacks against MGM Casino and Caesars Entertainment have been attributed to Scattered Spider, utilizing the BlackCat/ALPHV locker to encrypt systems.
Microsoft, referring to them as Octo Tempest, labelled Scattered Spider as one of the most dangerous financial criminal groups, known for resorting to violent threats to achieve their goals.
Source: Microsoft
Scattered Spider Tactics
The FBI and CISA advisory underscores Scattered Spider’s potent initial access tactics, involving posing as IT or help-desk staff to trick company employees into providing credentials or network access. The group utilizes various methods, including phone calls, SMS phishing, email phishing, MFA fatigue attacks, and SIM swapping.
After gaining a foothold, Scattered Spider employs a range of publicly available software tools for reconnaissance and lateral movement. Legitimate tools like Fleetdeck.io, Level.io, Mimikatz, Ngrok, Pulseway, Screenconnect, Splashtop, and Tactical.
RMM, Tailscale, and Teamviewer are utilized maliciously. Additionally, the group conducts phishing attacks to install malware such as WarZone RAT, Raccoon Stealer, and Vidar Stealer to steal login credentials and other valuable data.
Recent observations indicate a new tactic involving data exfiltration and file encryption using the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware, followed by negotiation attempts through messaging apps or email.
Mitigations
The FBI and CISA recommend specific mitigations to counter the threats posed by Scattered Spider.
Key recommendations include using application controls with allowlisting, monitoring remote access tools, implementing phishing-resistant MFA, securing and limiting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) usage, maintaining offline backups, adhering to strong password practices, regularly updating systems and software, implementing network segmentation, and enhancing email security.
Organizations are advised to test and validate their security controls against MITRE ATT&CK techniques described in the advisory.








